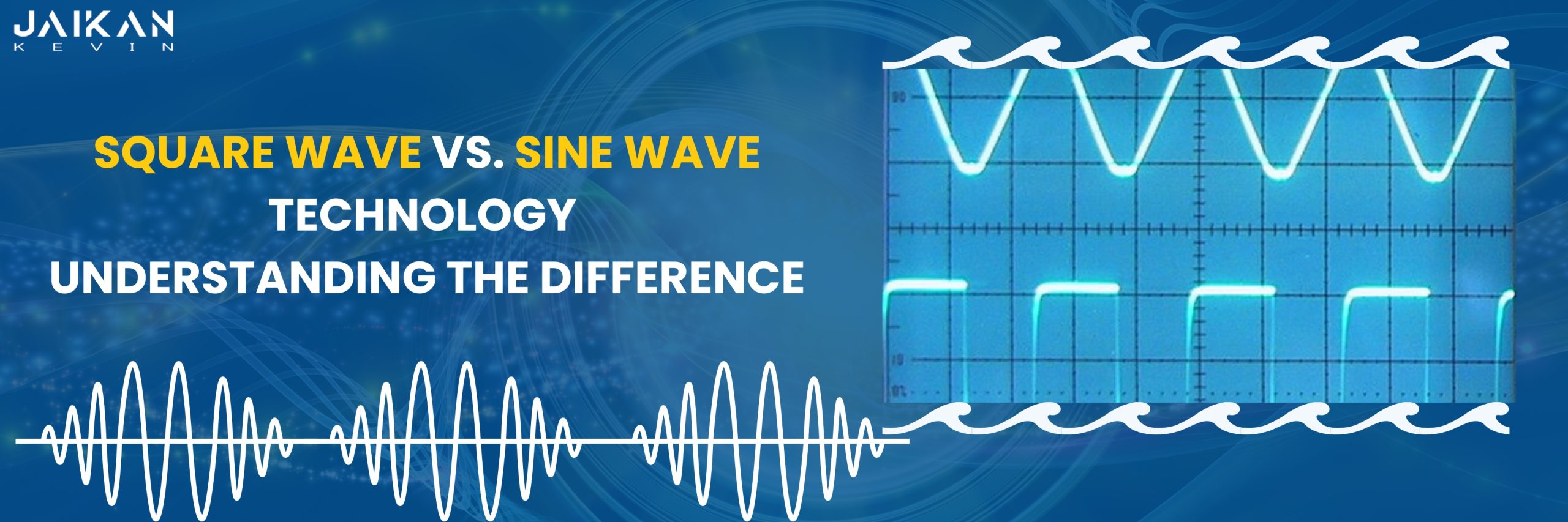
In the realm of power inverters, the choice between square wave and sine wave technology is a critical consideration that can impact the performance, compatibility, and overall effectiveness of your electrical systems. While both technologies serve the purpose of converting DC power to AC power, they do so in markedly different ways, each with its own set of advantages and limitations. Let’s delve into the comparison between square wave and sine wave technology to understand their differences and determine which is the better option for your needs.
Waveform Characteristics
Square Wave Technology: Square wave inverters produce an output waveform that resembles a series of square pulses. These pulses alternate between maximum positive and negative voltages, resulting in a waveform that is characterized by abrupt changes in voltage levels.
Sine Wave Technology: Sine wave inverters, on the other hand, produce an output waveform that closely mimics the smooth, undulating pattern of a sine wave. This waveform is characterized by gradual transitions between positive and negative voltage levels, resembling the natural flow of alternating current (AC) electricity.
Compatibility
Square Wave Technology: Square wave inverters are generally less compatible with sensitive electronic devices due to the irregular waveform they produce. While they may be suitable for powering basic appliances and tools, square wave inverters can cause issues such as overheating, noise, and reduced efficiency in more sophisticated equipment.
Sine Wave Technology: Sine wave inverters are highly compatible with a wide range of electronic devices, including computers, televisions, audio equipment, and medical devices. The smooth, consistent waveform produced by sine wave inverters ensures optimal performance and reliability in sensitive electronics, making them the preferred choice for most applications.
Efficiency and Performance
Square Wave Technology: Square wave inverters are typically less efficient than sine wave inverters due to the higher harmonic content and increased distortion in their output waveform. This can result in reduced efficiency, increased heat generation, and potential damage to connected devices over time.
Sine Wave Technology: Sine wave inverters offer superior efficiency and performance compared to square wave inverters. The clean, stable waveform produced by sine wave inverters ensures efficient power transfer and minimal distortion, resulting in reliable operation and extended lifespan for connected equipment.
Noise and Interference
Square Wave Technology: Square wave inverters may introduce noise and electromagnetic interference (EMI) into audio and radio equipment due to the sharp edges and high-frequency components present in their output waveform. This can lead to poor audio/video quality and disrupted communication signals.
Sine Wave Technology: Sine wave inverters produce minimal noise and EMI, providing clean, interference-free power to sensitive electronics. The smooth waveform produced by sine wave inverters ensures high-quality audio/video reproduction and reliable communication signals, making them ideal for applications where signal integrity is critical.
In summary, while both square wave and sine wave inverters serve the purpose of converting DC power to AC power, sine wave technology emerges as the superior choice for most applications due to its compatibility, efficiency, performance, and reliability. While square wave inverters may offer a more budget-friendly option for basic power needs, sine wave inverters provide the clean, stable power required for sensitive electronic equipment and critical applications. When choosing between square wave and sine wave technology, it’s essential to consider your specific power requirements, equipment compatibility, and performance expectations to make an informed decision that meets your needs effectively.